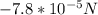Step-by-step explanation:
For Particle A:
The net gravitational force is the sum of the two forces due to particle B and due to particle C. Both of these particles have positive direction.
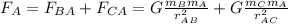
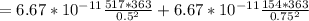
=
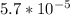 N
N
For Particle B:
The net gravitational force is the sum of the two forces: due to particle A and due to particle C. The force due to particle A is negative as its direction is to left. The force due to particle C is positive.
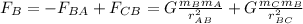
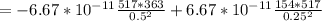
=
 N
N
For particle C:
The net gravitational force is the sum of two forces: due to particle A and due to particle B. Both forces are negative then,
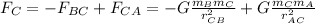
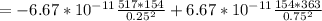
=