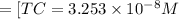Step-by-step explanation:
The value of first dissociation constant;
![pK_(a1)=-\log[K_(a1)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/autw9oh9xvfzcuedgpb8basibh917n1hdr.png)
![6.35=-\log[K_(a1)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/mih1i7i1crt18fr54lohde9kdd3f697j2m.png)
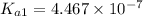
The value of seconddissociation constant;
![pK_(a2)=-\log[K_(a2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/plcbh91n3pa3onw1tuve34xavc8ey33dor.png)
![10.33=-\log[K_(a2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/vmxu2d90tqx9y1v1n4z3p9hgyyjfo085tm.png)

The pH of the water = 7.5
![pH=\log[H^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/rfq3q1wzaise9tr96c3u2793zsfu8ikuwi.png)
![7.5=\log[H^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/id2pw9t76ynptaquekia9l1o2j3546uwmv.png)
![[H^+]=3.162* 10^(-8) M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/e9c1o7br2svwubzln3jcz4244w52sorz89.png)
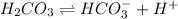
C 0 0
At equilibrium
(C-x) x x
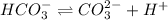
x 0 0
At equilibrium
(x -y) y y
Expression of an second dissociation constant will be given as:
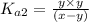
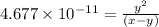 ..[1]
..[1]
![x+y=[H^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/auc0gwtydn14yej7trh4nues81e8glmvmo.png)
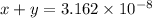 ...[2]
...[2]
Solving [1] and [2]:
x =
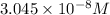
y =
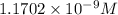
Expression of an first dissociation constant will be given as:
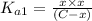
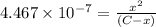
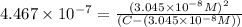
Solving for C:
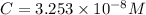
At equilibrium , concentration of species:
Carbonic acid :
![[H_2CO_3]=(C-x)=3.253* 10^(-8) M-3.045* 10^(-8) M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/5czufdqxm5tbnwf30py6adteblap4sn7uh.png)
![[H_2CO_3]=2.08* 10^(-9) M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/6niyxeqljz1q8k6zdg8ueahlua9l5j17t8.png)
Carbonate ion :
![[CO_3^(2-)]=y=1.1702* 10^(-9) M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/1fn2yxcpuchv9y6rmw8sqs8smeec3afuyg.png)
Bicarbonate :
![[HCO_3^(-)]=(x-y)=3.045* 10^(-8) M-1.1702* 10^(-9) M=2.928* 10^(-8) M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/jp2odafryjjb2pxf1g5blyo95h1sjwnlx4.png) Total carbonates:[TC]
Total carbonates:[TC]
![[TC]=[H_2CO_3]+[HCO_3^(-)]+[CO_3^(2-)]=C](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/s4c4ujnelxryy0anu2p0ql59jxmxtfysb7.png)