Answer: The molarity and molality of sucrose solution is 0.146 M and 0.129 m respectively
Step-by-step explanation:
- Calculating the molarity of solution:
To calculate the molarity of solution, we use the equation:
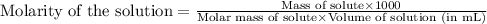
Given mass of sucrose = 15 g
Molar mass of sucrose = 342.3 g/mol
Volume of solution = 300 L
Putting values in above equation, we get:
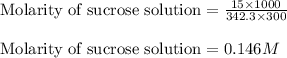
Hence, the molarity of sucrose solution is 0.146 M
- Calculating the molality of solution:
To calculate the mass of solvent, we use the equation:
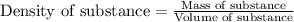
Density of solvent = 1.13 g/mL
Volume of solvent = 300 mL
Putting values in above equation, we get:
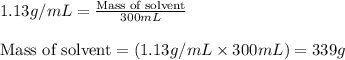
To calculate the molality of solution, we use the equation:
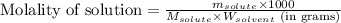
where,
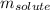 = Given mass of solute (sucrose) = 15 g
= Given mass of solute (sucrose) = 15 g
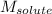 = Molar mass of solute (sucrose) = 342.3 g/mol
= Molar mass of solute (sucrose) = 342.3 g/mol
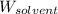 = Mass of solvent = 339 g
= Mass of solvent = 339 g
Putting values in above equation, we get:
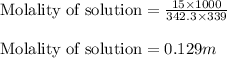
Hence, the molality of sucrose solution is 0.129 m