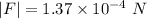Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
Length of the parallel wires (L) = 3.7 m
Current in the first wire (I₁) = 3.6 A
Current in the second wire (I₂) = 1.6 A
Separation between the parallel wires (d) = 3.1 cm = 0.031 m [1 cm = 0.01 m]
Both the wires will attract each with forces equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
Now, the magnitude of the force acting between the two wires is given as:
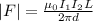
Where,
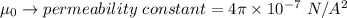
Plug in the given values and solve for |F|. This gives,
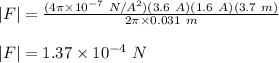
Therefore, the magnitude of the force between the two wires is