Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
1. Balanced molecular equation
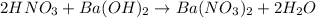
2. Mole ratio
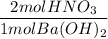
3. Moles of HNO₃
- Number of moles = Molarity × Volume in liters
- n = 0.600M × 0.0100 liter = 0.00600 mol HNO₃
4. Moles Ba(OH)₂
- n = 0.700M × 0.0310 liter = 0.0217 mol
5. Limiting reactant
Actual ratio:
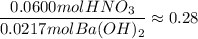
Since the ratio of the moles of HNO₃ available to the moles of Ba(OH)₂ available is less than the theoretical mole ratio, HNO₃ is the limiting reactant.
Thus, 0.006 moles of HNO₃ will react completely with 0.003 moles of Ba(OH)₂ and 0.0217 - 0.003 = 0.0187 moles will be left over.
6. Final molarity of Ba(OH)₂
- Molarity = number of moles / volume in liters
- Molarity = 0.0187 mol / (0.0100 + 0.0031) liter = 0.456M