Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The equilibrium constant for an equilibrium reaction is the ratio of the equilibrium constant for the forward reaction, Kf, to the equilibrium constant for the reverse reaction, Kr:
- The forward reaction is: A → B, with rate constant is Kf = K₁ and
- The reverse reaction is: B → A, with rate constant Kr = K₂
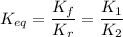
When you write the reaction in the other reaction, the forward and the reverse reaction are exchanged:
- The forward reaction is B → A, with rate constant Kf = K₂
- The reverse reaction is A → B, with rate constant Kr = K₁
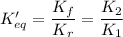
As you see:
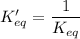
Thus, the equilibrium-constant expression for a reaction written in one direction is the reciprocal___ of the one for the reaction written for the reverse direction.