Answer:
Limiting reagent: fluorine.
Theoretical yield of ClF₃: 4.62 g.
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, one could identify the limiting reagent by comparing the available chlorine with the consumed chlorine by the fluorine considering the ideal gas equation and the 1 to 3 respectively stoichiometric relationship between them as shown below:
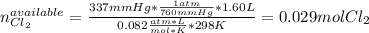
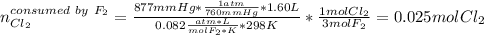
In such a way, there are 0.004 excess moles of chlorine, which means that fluorine is the limiting reagent. Therefore, the theoretical yield of ClF₃ turns out:
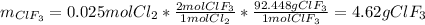
Best regards.