Answer:
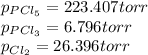
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, the undergoing chemical reaction is:
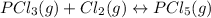
And the equilibrium constant at the reaction's temperature is:
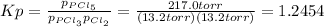
Now, even when chlorine is added, such pressure equilibrium constant does not change, therefore, since the initial total pressure is:
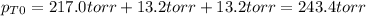
The new pressures, due to the change
 owing to the chlorine's addition, turn out:
owing to the chlorine's addition, turn out:
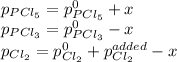
Therefore, the added chlorine is:
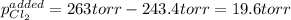
Thus, the new partial pressures are found via the law of mass action in terms of the change
 as follows:
as follows:
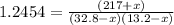
Solving for
 one obtains:
one obtains:
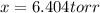
Finally, the new partial pressures result:
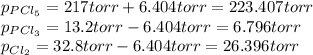
Best regards.