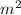Answer:
The heat flux between the surface of the pond and the surrounding air is 60 W/
Step-by-step explanation:
Heat flux is the rate at which heat energy moves across a surface, it is the heat transferred per unit area of the surface. This can be calculated using the expression in equation 1;
q = Q/A ...............................1
since we are working with the convectional heat transfer coefficient equation 1 become;
q = h (
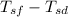 ) ........................2
) ........................2
where q is the heat flux;
Q is the heat energy that will be transferred;
h is the convectional heat coefficient = 20 W/
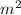 .K;
.K;
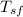 is the surface temperature =
is the surface temperature =
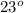 C 23°C + 273.15 = 296.15 K;
C 23°C + 273.15 = 296.15 K;
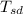 is the surrounding temperature =
is the surrounding temperature =
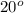 C = 20°C + 273.15 = 293.15 K;
C = 20°C + 273.15 = 293.15 K;
The values are substituted into equation 2;
q = 20 W/
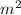 .K ( 296.15 K - 293.15 K)
.K ( 296.15 K - 293.15 K)
q = 20 W/
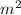 .K ( 3 K)
.K ( 3 K)
q = 60 W/
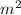
Therefore the heat flux between the surface of the pond and the surrounding air is 60 W/