Answer:
Option A) A Type I error for this situation would be to incorrectly conclude that the process is out of control.
Explanation:
We are given the following in the question:
Sample size, n = 15
Test:
average proportion of defective parts exceeds 10% that is whether the process is "out of control" or not.
Type I error:
- Also known as false positive error.
- It is the error of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true.
We can design the null and alternate hypothesis as:
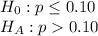
Type I error would be rejecting that the fact average proportion of defective parts is less than equal to 10% when it is true.
That is we accept the alternate hypothesis that average proportion of defective parts exceeds 10% when actually it does not.
Thus, we conclude that the process is out of control when it is not by committing a type I error.
Thus, the correct answer is:
Option A) A Type I error for this situation would be to incorrectly conclude that the process is out of control.