Answer:
- Second Newton's law of motion
Step-by-step explanation:
There are three Newton's laws of motion.
First Newton's law of motion, also named law of inertia, states that a body will stay at rest or uniform rectilinear motion, unless an unbalancing force acts on it.
Second Newton's law of motion states that the when an object is under the acction of an unbalanced for force, it will acquire a mass that is proportional to the magnitude of the net force and inversely related to the mass of the object.
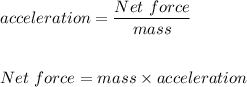
Third Newton's law of motion is the action-reaction law: whenever an object exerts a force on a second object, the second object will exert a force of the same magnitude and opposite direction on the first object.
As the force acting upon an object is increased, the acceleration of the object is increased. As the mass of an object is increased, the acceleration of the object is decreased.