Answer : The time taken would be, 1.10 s
Explanation :
The integrated rate law equation for second order reaction follows:
![k=(1)/(t)\left ((1)/([A])-(1)/([A]_o)\right)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/a2lj3jeijlgwg6ljnsxcls8m69g41v1xla.png)
where,
k = rate constant =
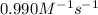
t = time taken = ?
[A] = concentration of substance after time 't' = 0.380 M
![[A]_o](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/4pmjkus4n3cfntqcbgc1rjdz49krp7grr3.png) = Initial concentration = 0.650 M
= Initial concentration = 0.650 M
Now put all the given values in above equation, we get:
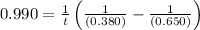
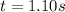
Hence, the time taken would be, 1.10 s