The law of conservation of energy is demonstrated by the movement of the pendulum as follows:
In a simple pendulum that has zero friction, mechanical energy is conserved. Total mechanical energy is calculated by combining kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy. As the pendulum swings back and forth, there is a constant exchange between kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy. So even when the pendulum is not moving, it has some sort of energy thus proving energy is neither created nor destroyed.
The law of conservation of energy states that "Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed".
The potential energy of the pendulum can be modeled off of the basic equation
PE = mgh
where g is the gravitational acceleration and h is the height.
The kinetic energy would be
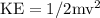 ,where m is the mass of the pendulum, and v is the speed of the pendulum.
,where m is the mass of the pendulum, and v is the speed of the pendulum.