Answer:
A. .1070
Explanation:
For each customer, there are only two possible outcomes. Either they make a purchase, or they do not. The probability of a customer making a purchase is independent from other customers. So we use the binomial probability distribution to solve this question.
Binomial probability distribution
The binomial probability is the probability of exactly x successes on n repeated trials, and X can only have two outcomes.
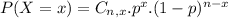
In which
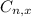 is the number of different combinations of x objects from a set of n elements, given by the following formula.
is the number of different combinations of x objects from a set of n elements, given by the following formula.
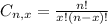
And p is the probability of X happening.
Forty-four percent of customers who visit a department store make a purchase.
This means that
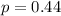
What is the probability that in a random sample of 9 customers who will visit this department store, exactly 6 will make a purchase?
This is
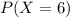 when n = 9. So
when n = 9. So
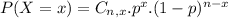
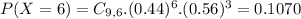
So the correct answer is:
A. .1070