The initial weight of mercury oxide in the sample is 4. 86.6 g (grams)
Step-by-step explanation:
2HgO → 2Hg + O₂
From the given pressure, temperature and volume, we can find the number of moles of oxygen. Using the molar ratio, we can find the moles of HgO and then from that moles and molar mass we can find the mass of HgO.
P = 0.970 atm, T = 390 K , V= 6.60 L
PV = nRT
We need to find n as,
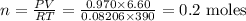
n = 0.2 moles of O₂
To find the moles of HgO,
The molar ratio is 1:2 for O₂ and HgO.
Moles of HgO =
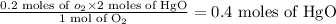
Now we have to multiply the moles by the molar mass of HgO as,
0.4 moles ×216.59 g / mol = 86.6 g of HgO
Thus it is clear that the initial weight of mercury oxide is 86.6 g