Here is the full question.
What is the pH of a solution that results when 0.010 mol HNO3 is added to 500 mL of a solution that is 0.10 M in aqueous ammonia and 0.20 M in ammonium nitrate? Assume no volume change. The Kb of ammonia is 1.8*10^-5.
Answer:
8.82
Step-by-step explanation:
Volume = 500 mL = 0.500 L
Number of moles of NH₃ = 0.10 mole × 0.500 L = 0.050 moles
Number of moles of NH₄⁺ = 0.20 mole × 0.500 L = 0.10 moles
NH₃ + H⁺ ----------> NH₄⁺
In 0.010 mole of HNO₃ ;
Number of moles of NH₃ = 0.050 moles - 0.010 moles
= 0.040 moles
Number of moles of NH₄⁺ = 0.10 moles + 0.010 = 0.11 moles
Concentration of NH₃ =
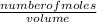
=
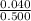
= 0.080 M
Concentration of NH₃ =
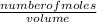
=
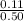
= 0.220 M
NH₃ + H₂O ⇄ NH₄⁺ + OH⁻
Initial 0.080 M 0 0.220 M 0
Change -x +x x
Equilibrium 0.080 -x 0.220 +x x
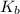 =
=
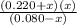
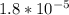 =
=
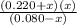
x = [OH⁻] = 6.55 × 10⁻⁶ M
pOH = 5.18
pH + pOH = 14
pH = 14 - pOH
pH = 14 - 5.18
pH = 8.82