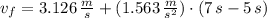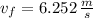Answer:
a)
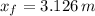 , b)
, b)
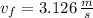 , c)
, c)
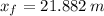 , d)
, d)
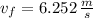
Step-by-step explanation:
a) Position of the puck:
The acceleration experimented by the puck is:
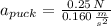
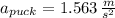
As the force remains constant during its time of application, accelaration is also constant. Position at given time is the following:
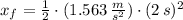
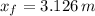
b) Speed of the puck:
The speed of the puck is computed as follows:
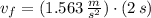
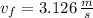
c) The absence of external force and the fact that ground is frictionless lead to the conclusion that hockey puck moves out at constant speed from 2 s. to 5 s. Then, the initial speed is:
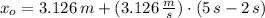
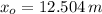
Likewise, the initial speed is
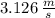 .
.
The new application of the same force means the return of a accelerated movement. Then:
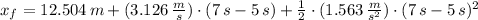
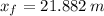
d) The final speed of the puck is: