Step-by-step explanation:
According to Bronsted-Lowry, an acid is defined as the specie which is able to donate hydrogen ions when dissolved in water.
For example,
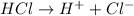
On the other hand, bases are the species which are able to donate hydroxide ions when dissolved in water.
For example,
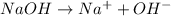
It is known that the full form of PABA is para-aminobenzoic acid. It's chemical formula is
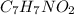 . This compound can take up a proton and also it is able to lose a proton.
. This compound can take up a proton and also it is able to lose a proton.
Therefore, PABA acts as both an acid and a base.
The carboxylic group has a chemical formula COOH and it can easily donate a hydrogen ion. Therefore, it is an acid.
And,
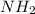 contains a lone pair of electrons and it is difficult for it to lose a hydrogen ion but it can readily gain a hydrogen ion. Therefore, this group acts as a base.
contains a lone pair of electrons and it is difficult for it to lose a hydrogen ion but it can readily gain a hydrogen ion. Therefore, this group acts as a base.
Thus, we can conclude that PABA is both an acid and a base. The molecule contains both a C O O H; carboxylic group and an − N H 2; amine group. It can act like an
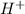 donor or acceptor.
donor or acceptor.