Answer:
0.05 M is the concentration of iodide in the solution in the test tube.
Step-by-step explanation:
Molarity of KI = 0.20 M
Volume of KI solution = 2.00 mL = 0.002 L ( 1 mL = 0.001 L)
Moles of KI = n
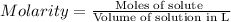
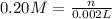
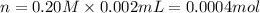
Volume of solutions formed by mixing all the solutions in a test tube = V
V = 2.00 mL+1.00 mL+0.50 mL+0.50 mL+2.00 mL+2.00 mL = 8.00 ml
V = 8.00 mL = 0.008 L
Concentration of KI in the test tube = [KI]
![[KI]=(0.0004 mol)/(0.008 L)=0.05 M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/30zg2pnbcaprhx9vqm6f75uchuduyc8wnv.png)
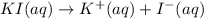
![[I^-]=[KI]=0.05 M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/y1c5bhqlauy2bevc26gqesar0xjl9amo1u.png)
0.05 M is the concentration of iodide in the solution in the test tube.