Answer:
Req = 6.2 Ω
Step-by-step explanation:
- We can find the equivalent resistance of the resistors connected in parallel, applying the principle of the conservation of the charge, which in ths case translates in that the overall current will be the sum of the currents flowing through esch resistor.
- Applying Ohm's law to each resistor, we reach to the following expression for the equivalent resistance:
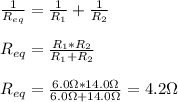
- If we put this fictitious resistor in series with a 2.0 Ω resistor, as the current must be the same for both resistors, applying Ohm's Law to both resistors, we find that the equivalent resistance is just the sum of the resistance of both resistors:
- R = 4.2 Ω + 2.0 Ω = 6.2 Ω