Answer:
The diameter of the cylindrical wire is 0.0446 cm or 44.6 mm
Step-by-step explanation:
Given;
current density of the fuse, J = 480 A/cm²
current in the fuse, I = 0.75 A
Current density, J = Current (I) / Area (A)
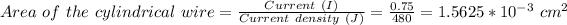
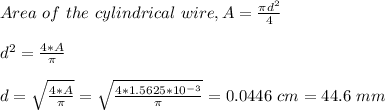
diameter of the wire = 0.0446 cm or 44.6 mm
Therefore, the diameter of cylindrical wire that should be used to make a fuse that will limit the current to 0.75 A, when the current density rises to 480 A/cm² is 44.6 mm