Answer:
Two-sided null hypothesis (i.e., the same sample size, the same standard deviation, and the same mean) will also be rejected at the same significance level.
Explanation:
The decision rule to reject a null hypothesis at α% level of significance is, if the p-value of the test is less than the level of significance then the null hypothesis of the test is rejected. And if p-value of the test is more than the level of significance then the null hypothesis of the test is failed to be rejected.
Now for a two-tailed test the p-value is,
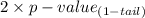 , i.e. the p-value is decreased for a two tail test.
, i.e. the p-value is decreased for a two tail test.
If a null hypothesis of a one-sided test is rejected at a significance level α, then it would mean that the p-value < α.
As the p-value < α then the two-tailed p-value is definitely less than α.
So the two-tail null hypothesis will also be rejected at the same level of significance.