Answer:
The right answer is option A
Step-by-step explanation:
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium states that the variations in genetic distribution will always be constant as long as there are no external factors to disturb it across generations like mutations, genetic drift and gene flow among others. This principle is an ideal situation and is not really applicable in reality.
A simple formula for the Hardy-Weinberg principle is
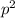 + 2pq +
+ 2pq +
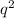 = 1 and p + q = 1 where p is the frequency of the dominant allele and q is the frequency of the recessive allele. While
= 1 and p + q = 1 where p is the frequency of the dominant allele and q is the frequency of the recessive allele. While
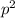 and
and
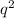 are the frequencies of the dominant and recessive genes respectively.
are the frequencies of the dominant and recessive genes respectively.
The frequency of a recessive genetic condition of 0.04 in a population means 4% of the population has a recessive genetic condition.
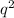 = 0.04 Genetic condition
= 0.04 Genetic condition
q = square root of 0.04 = 0.2 Since q is the frequency of the allele then the frequency is 20%