Answer:

Step-by-step explanation:
Raoult's law is a tool that allows to determine vapour pressure of solutions. The formula is:
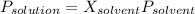 (1)
(1)
Where
P is Pressure of solution and solvent and X is mole fraction.
Moles of solute and solvent are:
Biphenyl:
11.5g×(1mol /154.21g) = 0.0746mol
Benzene
31.9g×(1mol /78.11g) = 0.408mol
Mole fraction of benzene is:
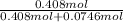 = 0.846
= 0.846
Replacing in (1):
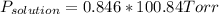

I hope it helps!