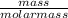Answer:
B : Their constant motion
C: Ideal gas law
Step-by-step explanation:
Question 1:
Gas particles collides with the walls of their containers due to their constant motion.
Gases moves randomly and haphazardly in all direction and they collide with themselves and the walls of their container.
The kinetic theory of gases provides a better oversight into this;
- The pressure of the gases is caused by the frequent collision between the gases and their container.
- The molecules of gases collides with one another and with walls of their container elastically without any loss of kinetic energy.
Based on this premise, we can clearly decipher that gas particles collides with the walls of their containers because they are always in constant motion
Question 2:
Given parameters:
Mass of the Helium gas = 5g
Volume of gas = 10mL
Pressure on gas = 20mmHg
Unknown:
Appropriate gas law to solve this problem = ?
Solution:
The ideal gas law would be the perfect plug to derive the unknown temperature.
This gas law is a derivative of the of three gas laws which are;
- Boyle's law
- Charles's law
- Avogadro's law
The law is written as:
PV = nRT
P is the pressure
V is the volume
R is the gas constant
n is the number of moles
T is the unknown temperature in this problem
- The ideal gas law is used to find any of the variables (P, V, n and T)
the number of moles is;
number of moles =