Answer:
The molar mass of the unknown gas is 392 g/mole
Step-by-step explanation:
Firstly we write out the parameters
Volume of the gas X that effuse for 105 s = 1.0 L
Volume of the O₂ gas that effuse for 30 s = 1.0 L
Molar mass of O₂ = 32 g/mole
Rate of effusion of the gas X = 1.0 L/105 s = 0.0095 L/s
Rate of effusion of O₂ gas = 1.0 L/30 s = 0.033 L/s
Graham's law of effusion states that
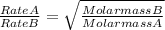
Therefore we have
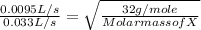 or Molar mass of X =
or Molar mass of X =
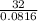 g/mole = 391.99 g/mole
g/mole = 391.99 g/mole
The molar mass of the unknown gas is 391.99 g/mole ≈ 392 g/mole