The question is incomplete, here is the complete question:
A chemistry student weighs out 0.104 g of sulfurous acid, a diprotic acid, into a 250.0 mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. He plans to titrate the acid with 0.0700 M NaOH solution. Calculate the volume of NaOH solution the student will need to add to reach the final equivalence point. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.
Answer: The volume of NaOH needed is 36.2 mL
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the molarity of solution, we use the equation:
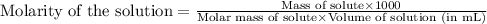
Given mass of sulfurous acid = 0.104 g
Molar mass of sulfurous acid = 82 g/mol
Volume of solution = 250 mL
Putting values in above equation, we get:
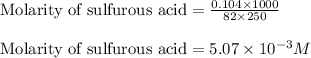
To calculate the volume of base, we use the equation given by neutralization reaction:
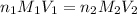
where,
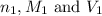 are the n-factor, molarity and volume of acid which is
are the n-factor, molarity and volume of acid which is
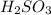
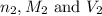 are the n-factor, molarity and volume of base which is NaOH.
are the n-factor, molarity and volume of base which is NaOH.
We are given:
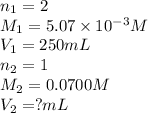
Putting values in above equation, we get:
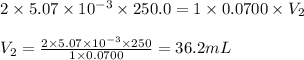
Hence, the volume of NaOH needed is 36.2 mL