Answer:
The equilibrium concentration of water vapor is 0.0125 M.
Step-by-step explanation:
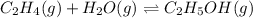
The concentration of ethene at an equilibrium =
![[C_2H_4]=0.015M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/x7k45d7l4v0ozkd6ak1ndpowzq2mugu05c.png)
The concentration of water vapor at an equilibrium =
![[H_2O]=?](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/61kq2vuzzuwgo8sryj2jpjfgarbj4n1vn7.png)
The concentration of ethanol at an equilibrium =
![[C_2H_5OH]=1.69 M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ixowgtfksub22lfpkdafsellzm6yvl9dmx.png)
the equilibrium constant of the reaction,
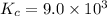
The expression of an equilibrium constant will be written as:
![K_c=([C_2H_5OH])/([C_2H_4][H_2O])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/lvk813o7r6hb7gktimx91s1dl13psr1nyy.png)
![9.0* 10^3=(1.69 M)/(0.015 M* [H_2O])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/21l2oj66fd18fwnjn3bjnctb13s4dasdy7.png)
![[H_2O]=(1.69 M)/(0.015 M* 9\timers 10^3)=0.0125 M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/pohp4inw8x8h9rppshs6rzgxu0pgn8i8zk.png)
The equilibrium concentration of water vapor is 0.0125 M.