Answer:
0.0668
Explanation:
Problems of normally distributed samples can be solved using the z-score formula.
In a set with mean
 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
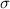 , the zscore of a measure X is given by:
, the zscore of a measure X is given by:
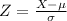
The Z-score measures how many standard deviations the measure is from the mean. After finding the Z-score, we look at the z-score table and find the p-value associated with this z-score. This p-value is the probability that the value of the measure is smaller than X, that is, the percentile of X. Subtracting 1 by the pvalue, we get the probability that the value of the measure is greater than X.
In this problem, we have that:
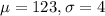
Find the probability that the diameter of a selected bearing is greater than 129 millimeters.
This is 1 subtracted by the pvalue of Z when X = 129. So
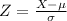
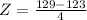
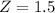
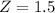 has a pvalue of 0.9332
has a pvalue of 0.9332
1 - 0.9332 = 0.0668
0.0668 = 6.68% probability that the diameter of a selected bearing is greater than 129 millimeters.