Answer:
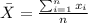
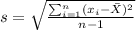
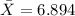 represent the sample mean for the sample
represent the sample mean for the sample
s=0.269 represent the sample standard deviation
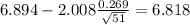
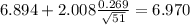
So on this case the 95% confidence interval would be given by (6.82;6.97)
Explanation:
For this case we have the following data:
7.4 6.86 6.99 6.81 6.62 7.1 6.94 6.72 6.71 7.28 6.78 6.85 7.13 7.07 6.76 6.99 6.61 7.41 6.27 7.01 6.31 7.18 7.01 6.71 6.39 6.98 6.82 6.98 6.91 6.58 7.11 6.89 6.86 7.01 6.49 6.64 6.91 6.58 7.01 7.23 6.69 7.3 7.33 7.1 6.9 6.85 7.29 6.71 7.09 6.92 6.55
A confidence interval is "a range of values that’s likely to include a population value with a certain degree of confidence. It is often expressed a % whereby a population means lies between an upper and lower interval".
The margin of error is the range of values below and above the sample statistic in a confidence interval.
Normal distribution, is a "probability distribution that is symmetric about the mean, showing that data near the mean are more frequent in occurrence than data far from the mean".
We can calculate the mean and the deviation from these data with the following formulas:
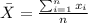
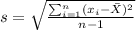
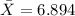 represent the sample mean for the sample
represent the sample mean for the sample
 population mean (variable of interest)
population mean (variable of interest)
s=0.269 represent the sample standard deviation
n=51 represent the sample size
The confidence interval for the mean is given by the following formula:
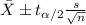 (1)
(1)
In order to calculate the critical value
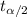 we need to find first the degrees of freedom, given by:
we need to find first the degrees of freedom, given by:
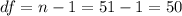
Since the Confidence is 0.95 or 95%, the value of
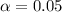 and
and
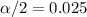 , and we can use excel, a calculator or a table to find the critical value. The excel command would be: "=-T.INV(0.025,50)".And we see that
, and we can use excel, a calculator or a table to find the critical value. The excel command would be: "=-T.INV(0.025,50)".And we see that
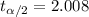
Now we have everything in order to replace into formula (1):
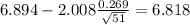
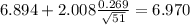
So on this case the 95% confidence interval would be given by (6.82;6.97)