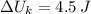Answer:
a)
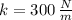 , b)
, b)
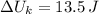 , c)
, c)
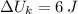 , d)
, d)
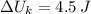
Explanation:
a) The spring constant is calculated by using this expression:
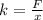
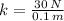
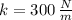
b) The work needed to compress the spring from its initial position is:
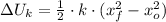
![\Delta U_(k) = (1)/(2)\cdot (300\,(N)/(m) )\cdot [(-0.3\,m)^(2)-(0\,m)^(2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/yzltn4fukj95egccjikw8g2kq5fhp67vnp.png)
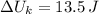
c) The work needed to stretch the spring is:
![\Delta U_(k) = (1)/(2)\cdot (300\,(N)/(m) )\cdot [(0.2\,m)^(2)-(0\,m)^(2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/j2vqvfbufepsk7viptppxh6i9nqx0e4qio.png)
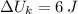
d) The work need to stretch the spring is:
![\Delta U_(k) = (1)/(2)\cdot (300\,(N)/(m) )\cdot [(0.2\,m)^(2)-(0.1\,m)^(2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/tjpgw2mfi8gud4kwlw3pc2w66th0xu7sgi.png)