Answer:
Terminal voltage = 11.5 V
Power across load = 119.7 W
Power across internal resistance = 5.4 W
Power delivered by battery = 125.2 W
Step-by-step explanation:
The current in the circuit is given by
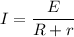
where E is the emf of the battery, R us the load resistance and r is the internal resistance.
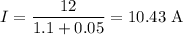
The terminal voltage is the potential difference across the load resistor.
V = I × R = 10.43 A × 1.1 Ω = 11.5 V
The power across any resistance is given by
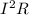
For the load resistor,
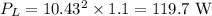
For the internal resistance,
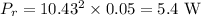
The power delivered by the battery is
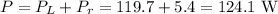
This could also be found by
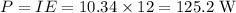
The discrepancy in both answers is due to the approximations. The second answer is better.