The classical motion for an oscillator that starts from rest at location x₀ is
x(t) = x₀ cos(ωt)
The probability that the particle is at a particular x at a particular time t
is given by ρ(x, t) = δ(x − x(t)), and we can perform the temporal average
to get the spatial density. Our natural time scale for the averaging is a half
cycle, take t = 0 → π/ ω
Thus,
ρ =
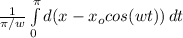
Limit is 0 to π/ω
We perform the change of variables to allow access to the δ, let y = x₀ cos(ωt) so that
ρ(x) =
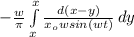
Limit is x₀ to -x₀
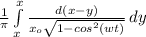
Limit is -x₀ to x₀
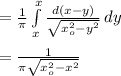
This has
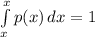 as expected. Here the limit is -x₀ to x₀
as expected. Here the limit is -x₀ to x₀
The expectation value is 0 when the ρ(x) is symmetric, x ρ(x) is asymmetric and the limits of integration are asymmetric.