Answer:
The pKa of the conjugate acid is 17.7
Step-by-step explanation:
If hydrogen is removed from water, the equilibrium concentration of the conjugate acid according to the information given in the question becomes,
Kₐ = [OH⁻]/[H₂O]
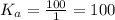
Now, we determine the equivalent pKa
pKa = -log[ka]
pKa = -log[100]
pKa = -2
Removal of hydrogen from water is reversible as shown below;
H₂O ⇄ OH⁻ + H⁺
15.7 -2
This reaction is reversible, and the difference in pKa = pKa[H₂O] - pKa[H⁺];
pKa of the conjugate acid = 15.7 - (-2) = 17.7
The pKa of the conjugate acid is 17.7