The given question is incomplete. The complete question is as follows.
Carbon absorbs energy at a wavelength of 150 nm. The total amount of energy emitted by a carbon sample is
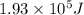 . Calculate the number of carbon atoms present in the sample, assuming that each atom emits one photon.
. Calculate the number of carbon atoms present in the sample, assuming that each atom emits one photon.
Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that the energy at which C-atom absorbs energy is 150 nm. So, energy emitted by the carbon atom will have same wavelength at which C-atom absorbs the energy.
As we know that relation between energy and wavelength is as follows.
E =
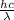
where, h = Planck's constant =
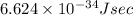
c = speed of light =
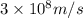
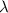 = 150 nm =
= 150 nm =
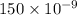
Therefore, energy of one carbon atom is calculated as follows.
E =
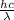
=
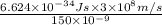
=
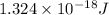
As the total energy emitted by the carbon sample is
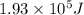 . Let us assume that the number of C-atoms in the sample be x and it is calculated as follows.
. Let us assume that the number of C-atoms in the sample be x and it is calculated as follows.
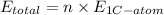
n =

=
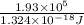
=

Thus, we can conclude that number of carbon atoms present in the sample, are
 .
.