Step-by-step explanation:
Expression to calculate the value of for the given reaction is as follows.
And, it is given that
[CO] =
![[H_(2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/qkqhb6wj8705cfmxjp8f7iaoav8mof5fvy.png) = 0.13 mol
= 0.13 mol
= 0.43 mol
Putting the given values into the above formula as follows.
![K_(c) = ([CO][H_(2)])/([H_(2)O])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/wbf51fxz5juj4afbii92aeah30wbv9lfw7.png)
=
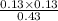
= 0.04
When additional amount of is added then all of has reacted.
So, new = 0 mols
new = 0.43 + 0.13 = 0.56 mols
The reaction equation is as follows.
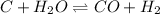
Initial: - 0.56 0.13 0
Change: - -x +x +x
Equilibm.: - 0.56 - x 0.13 + x x
So,
0.04 =
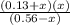
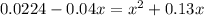
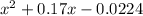 = 0
= 0
x = 0.087 mols
Therefore, the amount of [CO] at equilibrium is as follows.
0.13 + 0.087
= 0.217 mols
thus, we can conclude that the amount of CO in the flask when the system returns to equilibrium is 0.217 moles.