Answer:
The answers to the question are
a) The volume flow rate of the carbon dioxide at the compressor inlet is 0.2834 m³/s ≈ 0.3 m³/s
b) The power input to the compressor is 73.35 kW ≈ 70 kW
Step-by-step explanation:
We note the following
Mass flow rate = 0.5 kg/s
Inlet pressure = 100 pKa
Outlet pressure = 600 kPa
Inlet temperature = 300 K
Outlet temperature = 450 K
Molar mass of CO₂ = 44.01 g/mol
R Universal Gas Constant = 8.314 4621. J K−1 mol−1
a) Number of moles =
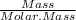 =
=
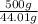 = 11.361 moles
= 11.361 moles
P·V= n·R·T ∴ V =
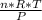 =
=
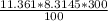 = 0.2834 m³
= 0.2834 m³
Therefore the volume flow rate = 0.2834 m³/s ≈ 0.3 m³/s
b) Cp at 300 K = 0.846 kJ/(kg K)
Cp at 600 K = 0.978 kJ/(kg K)
Cv = 0.657
K = 1.289
While the power input to the compressor can be calculated by
m'×Cp×(T₂-T₁)
Where m' = mass flow rate = 0.5 kg/s
Therefore power = 0.5 kg/s×0.978 kJ/(kg K)×(450 K - 300 K)
= 73.35 kJ/s = 73.35 kW ≈ 70 kW