Answer: The volume of NaOH required is 402.9 mL
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles for given molarity, we use the equation:
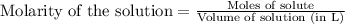 .....(1)
.....(1)
Molarity of HCl solution = 0.315 M
Volume of solution = 503.4 mL = 0.5034 L (Conversion factor: 1 L = 1000 mL)
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
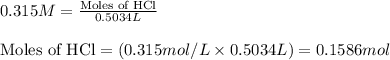
Molarity of sulfuric acid solution = 0.125 M
Volume of solution = 503.4 mL = 0.5034 L
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
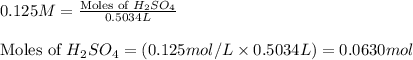
As, all of the acid is neutralized, so moles of NaOH = [0.1586 + 0.0630] moles = 0.2216 moles
Molarity of NaOH solution = 0.55 M
Moles of NaOH = 0.2216 moles
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
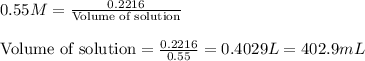
Hence, the volume of NaOH required is 402.9 mL