Answer:
Which stars are coming toward us? Which are moving away?
The Star A and B are moving toward the observer and Star C and D away from the observer.
Which star is moving fastest relative to us?
Star A is moving fastest relative to us.
What are the speeds of Star B and Star C?
The speed of the star B is 986842m/s and the speed of star C is 740131m/s.
Step-by-step explanation:
Which stars are coming toward us? Which are moving away?
Spectral lines will be shifted to the blue part of the spectrum if the source of the observed light is moving toward the observer, or to the red part of the spectrum when is moving away from the observer (that is known as the Doppler effect).
The wavelength at rest is 121.6 nm (
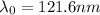 )
)
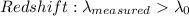
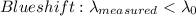
Then, for this particular case it is gotten:
Star A:
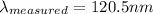
Star B:
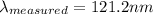
Star C:
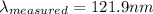
Star D:
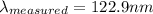
Star A:
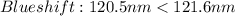
Star B:
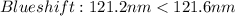
Star C:
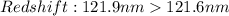
Star D:
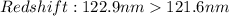
Therefore, according to the approach above. The Star A and B are moving toward the observer and Star C and D away from the observer.
Due to that shift the velocity of the star can be determined by means of Doppler velocity.
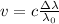 (1)
(1)
Where
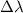 is the wavelength shift,
is the wavelength shift,
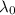 is the wavelength at rest, v is the velocity of the source and c is the speed of light.
is the wavelength at rest, v is the velocity of the source and c is the speed of light.
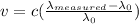
Which star is moving fastest relative to us?
Case for the Star A:
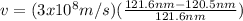
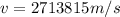
Case for the Star B:
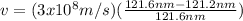
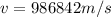
Hence, Star A is moving fastest relative to us.
What are the speeds of Star B and Star C?
Case for the Star C:
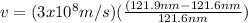
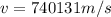
Therefore, The speed of the star B is 986842m/s and the speed of star C is 740131m/s.