Answer: The standard potential of the cell is 0.77 V
Step-by-step explanation:
We know that:
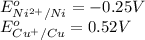
The substance having highest positive
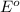 reduction potential will always get reduced and will undergo reduction reaction.
reduction potential will always get reduced and will undergo reduction reaction.
The half reaction follows:
Oxidation half reaction:
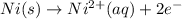
Reduction half reaction:
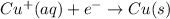 ( × 2)
( × 2)
To calculate the
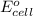 of the reaction, we use the equation:
of the reaction, we use the equation:
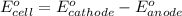
Substance getting oxidized always act as anode and the one getting reduced always act as cathode.
Putting values in above equation follows:
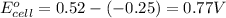
Hence, the standard potential of the cell is 0.77 V