Answer:
A) Kw (37°C) = 2.12x10⁻¹⁴
B) pH (37°C) = 6.84
Explanation:
The following table shows the different values of Kw in the function of temperature:
T(°C) Kw
0 0.114 x 10⁻¹⁴
10 0.293 x 10⁻¹⁴
20 0.681 x 10⁻¹⁴
25 1.008 x 10⁻¹⁴
30 1.471 x 10⁻¹⁴
40 2.916 x 10⁻¹⁴
50 5.476 x 10⁻¹⁴
100 51.3 x 10⁻¹⁴
A) The plot of the values above gives a straight line with the following equation:
y = -6218.6x - 11.426 (1)
where y = ln(Kw) and x = 1/T
Hence, from equation (1) we can find Kw at 37°C:
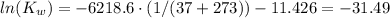
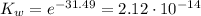
Therefore, Kw at 37°C is 2.12x10⁻¹⁴
B) The pH of a neutral solution is:
![pH = -log([H^(+)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/gffvdp6wxxhrziextmnwz7af71e53h7kfd.png) (2)
(2)
The hydrogen ion concentration can be calculated using the following equation:
![K_(w) = [H^(+)][OH^(-)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/atkfm3srdq4l17hsbc8il9e58e9b00i5lz.png) (3)
(3)
Since in pure water, the hydrogen ion concentration must be equal to the hydroxide ion concentration, we can replace [OH⁻] by [H⁺] in equation (3):
![K_(w) = ([H^(+)])^(2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/1vr9iogfs6magle96tdkh5rmzco4kwvul9.png)
which gives:
![[H^(+)] = \sqrt {K_(w)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/q6f5akvocvc3ctaemc8yaue17kh1ztxhub.png)
Having that Kw = 2.12x10⁻¹⁴ at 37 °C (310 K), the pH of a neutral solution at this temperature is:
![pH = -log ([H^(+)]) = -log(\sqrt {K_(w)}) = -log(\sqrt {2.12 \cdot 10^(-14)}) = 6.84](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/c5c9a3zusb19xfh6x6yrw45e6vadefjyl9.png)
Therefore, the pH of a neutral solution at 37°C is 6.84.
I hope it helps you!