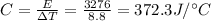Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
First of all, we need to calculate the total energy supplied to the calorimeter.
We know that:
V = 3.6 V is the voltage applied
I = 2.6 A is the current
So, the power delivered is
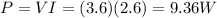
Then, this power is delivered for a time of
t = 350 s
Therefore, the energy supplied is
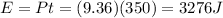
Finally, the change in temperature of an object is related to the energy supplied by
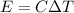
where in this problem:
E = 3276 J is the energy supplied
C is the heat capacity of the object
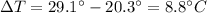 is the change in temperature
is the change in temperature
Solving for C, we find: