Answer:
A. 22 kg/cm2 (tensile)
Step-by-step explanation:
If the temperature drops to 18C degrees (by 2 degrees), it would shrink by an amount of

The strain would be:
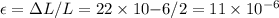
We can calculate the stress from strain and modulus of the elasticity:
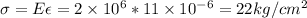
This stress would be tensile because the bar shrinks