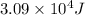Answer : The amount of heat required is,
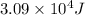
Solution :
The process involved in this problem are :
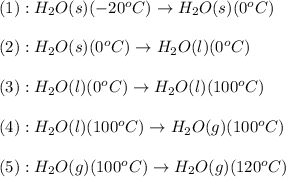
The expression used will be:
![\Delta H=[m* c_(p,s)* (T_(final)-T_(initial))]+m* \Delta H_(fusion)+[m* c_(p,l)* (T_(final)-T_(initial))]+m* \Delta H_(vap)+[m* c_(p,g)* (T_(final)-T_(initial))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/kwv66cjiel4wj7n4tljz1mjbjund3q35j0.png)
where,
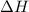 = heat required for the reaction
= heat required for the reaction
m = mass of ice = 10.0 g
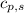 = specific heat of solid water or ice =
= specific heat of solid water or ice =
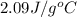
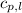 = specific heat of liquid water =
= specific heat of liquid water =
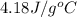
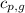 = specific heat of gaseous water =
= specific heat of gaseous water =
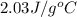
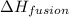 = enthalpy change for fusion =
= enthalpy change for fusion =
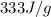
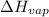 = enthalpy change for vaporization =
= enthalpy change for vaporization =
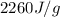
Now put all the given values in the above expression, we get:
![\Delta H=[10.0g* 2.09J/g^oC* (0-(-20))^oC]+10.0g* 333J/g+[10.0g* 4.18J/g^oC* (100-0)^oC]+10.0g* 2260J/g+[10.0g* 2.03J/g^oC* (120-100)^oC]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/s5rkjvmjhopvdrc0ljnljao3fvedpm0z1f.png)
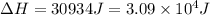
Therefore, the amount of heat required is,