Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The missing data on the question are:
- . . . fills a 200. mililiter flask
- . . . with 4.7 atm methane gas
- and 2.5 atm of water
- at 55.0ºC
- partial pressure of cabon dioxide to be 2.3 atm
Solution
1. Equilibrium equation:
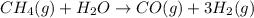
2. ICE (initial, change, equilibrium) table:
Partial pressures in atm
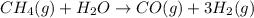
I 4.7 2.5 0 0
C -x -x +x +3x
E 4.7 - x 2.5 - x x 3x
3. Partial pressures:
The partial pressure of hdyrogen gas at equilibrium is 2.3 atm
Then:
- 3x = 2.3 atm
- x = 0.7667 atm
- 4.7 - x = 3.9333 atm
- 2.5 - x = 1.7333 atm
4. Pressure equilibrium constant equation:
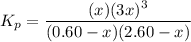
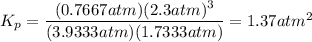
Round to two significant figures: 1.4 atm²