Answer:
It increases by 16 times
Step-by-step explanation:
The magnitude of the gravitational force between two objects is given by the equation
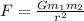
where
G is the gravitational constant
m1, m2 are the masses of the two objects
r is their separation
In this problem, we call:
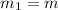 is the Earth's mass
is the Earth's mass
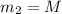 is the Sun's mass
is the Sun's mass
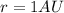 is the initial distance Earth-Sun
is the initial distance Earth-Sun
So the gravitational force between the two objects is
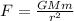
Later, the Earth is moved to a distance of
r' = 0.25 AU
which is equivalent to write
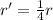
from the Sun.
Therefore, the new gravitational force will be:
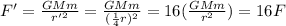
So, the gravitational force increases by a factor of 16.