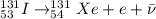Answer:
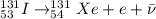
Step-by-step explanation:
In a beta (minus) decay, a neutron in a nucleus turns into a proton, emitting a fast-moving electron (called beta particle) alongside with an antineutrino.
The general equation for a beta decay is:
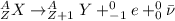 (1)
(1)
where
X is the original nucleus
Y is the daughter nucleus
e is the electron
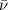 is the antineutrino
is the antineutrino
We observe that:
- The mass number (A), which is the sum of protons and neutrons in the nucleus, remains the same in the decay
- The atomic number (Z), which is the number of protons in the nucleus, increases by 1 unit
In this problem, the original nucles that we are considering is iodine-131, which is
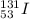
where
Z = 53 (atomic number of iodine)
A = 131 (mass number)
Using the rule for the general equation (1), the dauther nucleus must have same mass number (131) and atomic number increased by 1 (54, which corresponds to Xenon, Xe), therefore the equation will be: