Answer:
The over all reaction :
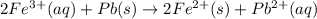
The standard cell potential of the reaction is 0,.897 Volts.
Step-by-step explanation:
Reduction at cathode :
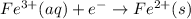 ..[1]
..[1]
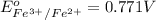
Reduction potential of
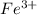 to
to
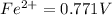
Oxidation at anode:
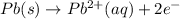 .[2]
.[2]
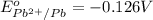
Reduction potential of
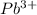 to
to
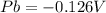
To calculate the
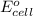 of the reaction, we use the equation:
of the reaction, we use the equation:
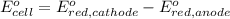
Putting values in above equation, we get:
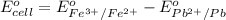
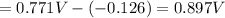
The over all reaction : 2 × [1] + [2]
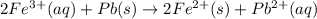
The standard cell potential of the reaction is 0,.897 Volts.