Answer:
P(A/B) is called the CONDITIONAL PROBABILITY of occurring of event A when event B has already taken place.
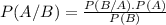
Explanation:
Let us assume there are two given events A and B.
The probability of A when B has occurred is given as P (A/B).
The probability of B when A has occurred is given as P (B/A)
Also, the probability of occurring A independently = P(A)
The probability of occurring B independently = P(B)
Now, the BAYES THEOREM gives us the exact formula to determine the CONDITIONAL PROBABILITY.
By Bayes Formula:
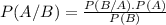
Here, P(A/B) is called the CONDITIONAL PROBABILITY of occurring of event A when event B has already taken place.