Answer:
5183 sec.
Step-by-step explanation:
- The power dissipated in the resistance, will be used to raise the temperature of the water completely.
- This power can be found applying Joule's law, which states the following:
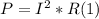
- If the resistance of the heating coil can be assumed as constant with the temperature, we can find the current I applying Ohm's Law, as follows:
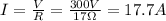
- Now, from (1) we can find P, as follows:
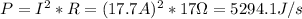
- The energy supplied by this power, is just the product of the power times the time during which the energy was delivered:
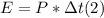
- This energy, will be supplied as heat to the mass of water, as stated by the following equation (assuming no heat losses out of the heater):
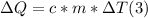
- where c= specific heat of water = 4186 J/ºC*kg, m= 115 kg, and ΔT= 57ºC.
- From (2) and (3), if left sides are equal each other, so do right sides:
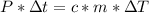
- Replacing by the values, we can solve for Δt, as follows:
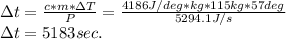
- The time required to raise the temperature of 115 kg of water, from 18ºC, to 75ºC, is 5183 sec (approximately 1hr 26').